In this Post you will be able to take quiz containing important MCQs of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and topic covered in this Quiz will be Odontogenic Infections in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Correct Answers are Marked in Bold and Blue colour.
Odontogenic Infections Multiple Choice Questions : Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
1. Odontogenic infections are most commonly caused by:
Answer: A. Mixed bacteria
B. Anaerobic bacteria
C. Aerobic bacteria
D. Streptococci
2. The infection from a lower third molar pericoronal area spreads mostly to _________ space.
A. Submandibular
B. Submental space
Answer: C. Pterygomandibular space
D. Buccal space
3. Involucrum is:
A. Dead bone
Answer: B. New live bone surrounding dead bone
C. Previous live bone
D. Sclerotic bone
4. The facial space that is divided by styloid process into an anterior and posterior compartment is:
A. Pterygomandibular
Answer: B. Lateral pharyngeal
C. Retropharyngeal
D. Infratemporal
5. The most definite clinical sign indicating odontogenic infection in to the masticatory space is:
Answer: A. trismus
B. xerostomia
C. difficulty in swallowing
D. swelling in submental area
6. Which of the following does not suggest post operative infection?
A. Increase in temperature
B. Swelling
C. Pain
Answer: D. Pitting edema
7. Ludwig’s angina is characterized by:
Answer: A. Raised tongue
B. Elevation of ear lobe
C. Trismus
D. Unilateral swelling
8. Trismus associated with infection of lateral pharyngeal space is related to irritation of the:
A. Buccinator
B. Masseter
C. Lateral pterygoid
Answer: D. Medial pterygoid
9. Garre’s osteomyelitis is:
Answer: A. Chronic focal sclerosis and non suppurative osteomyelitis
B. Chronic focal sclerosis and suppurative osteomyelitis
C. Characterized by suppuration and acute pain
D. Chronic diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis
10. Death in Ludwig’s angina occurs due to:
A. Sepsis
Answer: B. Respiratory obstruction
C. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
D. Carotid blow-out
11. The roof of pterygomandibular space is formed by:
A. Temporalis muscle
B. Medial pterygoid muscle
C. Cranial base
Answer: D. lateral pterygoid
12. Retropharyngeal space infection is mainly due to spread of:
A. Cervical tuberculosis
B. Meningoencephalitis
C. Mumps
Answer: D. Odontogenic infections
13. The distinguishing feature of masticatory space infection is:
A. Pain
B. Dysphagia
Answer: C. Trismus
D. Swelling
14. The greatest barrier to infection is:
A. Connective tissue
B. Epithelium
C. Muscle
Answer: D. Fascia
15. Osteoradionecrosis is due to:
A. Infection
Answer: B. Endarteritis of blood vessels
C. Sepsis
D. None of the above
16. A mandibular dental infection which exits the buccal cortical plate above the muscle attachment will cause abscess of:
A. Buccal space
B. Masseter space
Answer: C. Vestibular sulcus
D. Masticatory space
17. Which of the following is not a primary mandibular space?
A. Buccal
B. Sublingual
C. Submandibular
Answer: D. Pterygomandibular
18. Treatment of Garre’s osteomyelitis is:
A. Incision and drainage
B. Sequestrectomy
C. Saucerization
Answer: D. Surgical recontouring
19. In a 19 year old patient with a swelling over the left angle of the mandible, temperature of 38 degrees centigrade and negative history of trauma, one should suspect:
A. spontaneous fracture of the mandible
Answer: B. pericoronal infection
C. Mumps
D. Sjogren’s syndrome
20. Osteomyelitis:
A. never occurs in infants
B. in acute cases fracture of the mandible is very common
Answer: C. of mandible can show symptoms of lip paresthesia
D. produces no lymphadenopathy
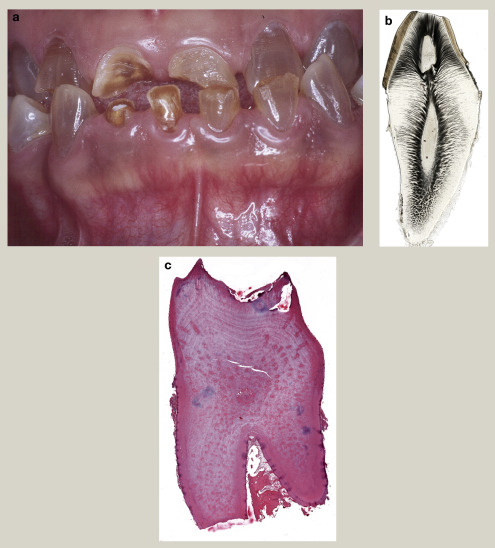
21. Dead bone is seen on the radiograph as:
A. more radiolucent
Answer: B. more radioopaque
C. with osteophytes growing out
D. soap bubble appearance
22. The most dangerous type of spread of infection from apical abscess is to:
A. Infratemporal fossa
B. Pterygoid
Answer: C. Parapharyngeal space
D. Submandibular space
23. Hyperbaric oxygen is indicated for:
A. Obstructive lung disease
Answer: B. Osteoradionecrosis
C. Cardiac failure
D. Renal disease
24. Cavernous sinus thrombosis following infection of anterior maxillary teeth most often from infection along:
A. Facial artery
B. Angular artery
Answer: C. Ophthalmic vein
D. Pterygoid plexus
25. A tender swelling in submandibular triangle is most likely diagnosed as:
Answer: A. Lymphadenopathy
B. Ludwig’s angina
C. Phlegmon
D. None of the above
26. Infection of masticatory space is usually associated with:
A. tonsillar abscess
Answer: B. mandibular molar
C. lateral pharyngeal space
D. Parotid space infection
27. A diagnosis of cavernous sinus thrombosis is made on the basis of:
i) known site of infection
ii) septicemia
iii) venous obstruction in retina, conjunctiva, or eyelid
iv) Paresis of third, fourth, and sixth nerves
v) Abscess formation of neighboring soft tissues
vi) Nuchal rigidity
A. 1,2,3,4,5
B. 3,4,5
C. 1,2,5,6
Answer: D. All of the above correct
28. Osteomyelitis of the jaw can be cured by:
A. Resection
B. Physiotherapy
Answer: C. Sequestrectomy with antibiotic treatment
D. Drainage
29. Lateral pharyngeal space is not connected directly to:
Answer: A. Buccal space
B. Sublingual space
C. Submandibular space
D. Retropharyngeal space
30. A periapical abscess of a mandibular second molar space spreads most commonly to the:
Answer: A. Submandibular space
B. Temporal space
C. Sublingual space
D. Infratemporal space
31. Palatal abscess most commonly results from infection of:
A. Maxillary centrals
Answer: B. Maxillary laterals
C. Maxillary canine
D. Maxillary premolars
32. Infection from maxillary first molar drains into:
A. Submandibular space
B. Infratemporal space
Answer: C. Buccal space
D. Infraorbital space
33. After incision and drainage of an abscess, the infectious process has failed to regress in spite of the patient being on high doses of an antibiotic. It would be wise to:
A. Insert a large drain
Answer: B. Repeat culture and sensitivity tests
C. Debride and irrigate the area with a fibrinolytic agent
D. Begin the parenteral administration of proteolytic enzymes to augment the antibiotics
34. Which of the following is not present in pterygomandibular space?
Answer: A. Auriculotemporal nerve
B. Lingual nerve
C. Mandibular nerve
D. Mylohyoid nerve
35. Which of the following features is not associated with acute osteomyelitis of mandible ?
A. Severe pain
B. Purulent exudate
C. Paresthesia of lower lip
Answer: D. Radiographic evidence of bone destruction
36. The incision for drainage in Ludwig’s angina extends:
A. upto neck
B. to the angle of mandible
Answer: C. floor of mouth
D. all of the above
37. Boundaries of the pterygomandibular space includes all of the following except:
A. Lateral pterygoid muscle
B. Parotid gland
Answer: C. Masseter muscle
D. Buccinator muscle
38. After extraction of upper central incisor, patient develops opthalmoplegia, meningitis and lateral rectus paralysis. The diagnosis is:
Answer: A. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
B. Not related
C. Cellulitis
D. Ludwig’s angina
39. Pericoronitis is seen in relation to:
A. Impacted third molars only
Answer: B. Around incompletely erupted crown
C. Completely erupted crowns only
D. None of the above
40. Subperiosteal abscess, penetrating deep is seen after extraction of:
A. Maxillary third molar
Answer: B. Mandibular third molar
C. Maxillary first molar
D. Mandibular first molar
41. In infection involving the submandibular space when extra oral incision and drainages are necessary, which of the following structures should be divided?
A. Skin only
B. Skin, superficial fascia only
C. Skin, superficial fascia, platysma and masseter muscle
Answer: D. Skin, superficial fascia, platysma, masseter and deep cervical fascia
42. In pericoronal abscess related to distoangular impacted lower third molars, the infection may spread to:
Answer: A. Submasseteric space
B. Sublingual space
C. Submental space
D. Buccal space
43. Untrue regarding Ludwig’s angina:
A. Involves submandibular, sublingual, and submental space
B. Involves bilateral mandibular spaces and lymphadenopathy
Answer: C. Bilateral submandibular, sublingual and submental spaces alongwith salivary gland enlargements
D. None
44. Sublingual space is divided from submandibular space by:
Answer: A. Fibres of mylohyoid
B. Submandibular gland
C. Body of mandible
D. Geniohyoid
45. Penrose drain is:
A. a simple rubber tube which opens at one end
Answer: B. simple rubber tube which opens at both ends
C. Modified corrugated rubber drain
D. Modified Foley’s catheter
46. A patient comes to the emergency with Ludwig’s angina. Which of the following is done first?
A. Incision and drainage
B. Antibiotic and IV fluid infusion
Answer: C. Fiberoptic nasotracheal intubation/tracheostomy under local anesthesia
D. Tracheostomy under general anesthesia
47. Sequestrum means:
Answer: A. necrosed bone, separated from its surrounding
B. a broken tooth piece
C. is new bone formed in osteomyelitis
D. is necrosed tooth
48. Masticatory space infection usually occurs from:
A. Infections of the last two lower molar
B. Non aseptic technique in local anesthesia
C. External or internal trauma to the mandibular angle region
Answer: D. All of the above
49. Dumb bell shaped swelling is characteristic of which type of odontogenic space infections?
A. Submandibular space infection
B. Buccal space infection
C. Submasseteric space infection
Answer: D. Temporal space infection
50. All of the following are present in pterygomandibular space except:
A. Nerve to mylohyoid
B. Chorda tympani
Answer: C. Long buccal nerve
D. Nerve to pterygoid
51. Cavernous sinus thrombosis can occur due to spread of odontogenic infection via:
A. Tissue Spaces
B. Lymphatic route
Answer: C. Hematogenous route
D. All of the above
52. Which of the following infection is the cause for multiple sites of osteomyelitis of the jaw:
A. Peritonsillar abscess
B. Local Trauma
Answer: C. Hematogenous infection
D. Buccal space infection
53. Standard airway for Ludwig’s angina :
A. Tracheostomy
Answer: B. Cricothyrotomy
C. Nasal intubation
D. Oral intubation
54. Which of the following is a secondary site of spread of odontogenic infection involving pterygomandibular space?
Answer: A. Infratemporal space
B. Canine space
C. Buccal space
D. Sublingual space
55. ‘Hot potato’ voice is characteristically seen in:
A. Pterygomandibular space infection
B. Retropharyngeal space infection
C. Pre tracheal space infection
Answer: D. Lateral pharyngeal space infection
56. Ludwig’s angina is usually caused by:
Answer: A. Streptococci and various mixed anaerobes
B. Anaerobic infection by Prevotella and Fusobacterium
C. Paramyxovirus
D. Candida species
57. The most common serious complication which can occur following surgery in maxillary incisor region is:
A. Iritis
B. Cellulitis
C. Periapical abscess
Answer: D. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
58. There is a swelling with respect to maxillary lateral incisor, since 48 hours. The swelling is hot and palpable, rebound on pressure. The treatment of choice is:
Answer: A. Incision and drainage
B. Antibiotic coverage
C. Antibiotics of heat only
D. Aspiration
59. In oral and maxillofacial surgery, ‘danger space’ is known as:
A. carotid sheath
B. Posterior to carotid sheath in posterior triangle of neck
C. posterior to transverse process of vertebrae
Answer: D. space between alar and prevertebral fascia